Solar Energy Myths Busted - Lead-Acid Batteries End Up As Toxic Waste
What's In A Lead-Acid Battery?
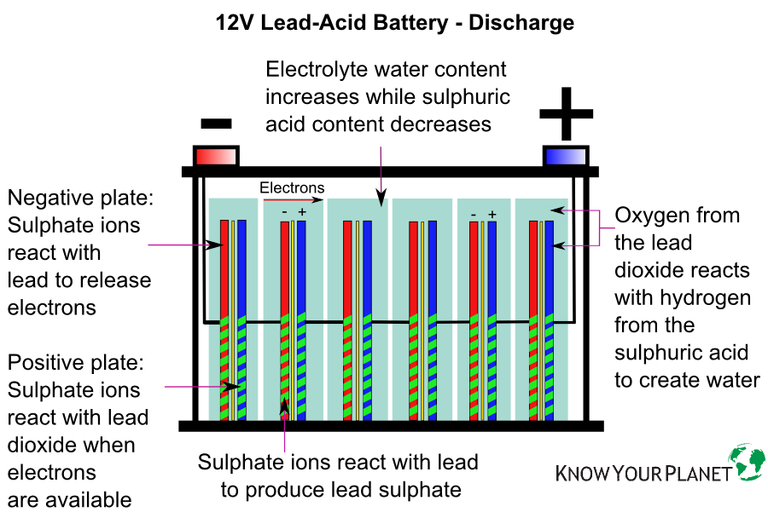
The cell of a lead-acid battery is formed from positive and negative plates made from lead and lead alloy. The plates are then submerged in a diluted electrolyte solution made from sulphuric acid and water to create an electrochemical cell.
Electrochemical cells are grouped together to form a battery. The cells are combined to either increase voltage or capacity, depending on how they are connected. For example, if a cell's voltage is rated at 2 and you need a 12 volt battery, then 6 cells are wired in series so that the voltage of each cell is combined to create the required 12 volts.
Not Just Any Old Lead-Acid Will Do
The above describes the basic construction of all lead-acid batteries, but not all lead-acid batteries are created equal. Automobile, or starter, batteries are lead-acid batteries that are designed for short bursts of energy discharged quickly, basically to start the car, and are made from thin lead plates not designed to be deeply discharged.
Batteries most commonly used in solar electric PV systems are deep cycle, which means they can tolerate being deeply discharged before being re-charged. They are made from thicker lead plates which allow the battery to be deeply discharged and which increase the life of the battery.
Sealed Or Unsealed
Liquid vented lead-acid batteries are not sealed and allow gasses to escape as the battery approaches a fully charged state. As gasses are vented, water is also lost and must be replenished so the battery must be refilled periodically, thus requiring maintenance.
Sealed lead-acid batteries are not totally sealed as they do have a valve in case of over-charging when excess pressure must be released. They are also known as valve regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries and are considered maintenance free, as there is no access to the electrolyte. For PV applications, sealed batteries come in 2 flavours - gel cell or absorbed glass mat (AGM). Gel cells' electrolyte is turned into gel by the addition of fumed silica; AGMs' electrolyte is suspended using thin fibrous felt (or silica glass mat), which acts like a sponge.
Battery Disposal
The lead-acid battery industry is heavily regulated and does a great job of recycling its products, as retail outlets in most states must by law accept dead lead-acid batteries for recycling. 60 to 80 percent of most lead-acid batteries is recycled, including over 90 percent of the lead, which is up to 4 times more than most other commodities that are commonly recycled. In fact, about 60 percent of the lead used to manufacture new lead-acid batteries comes from recycled lead, and, overall, 60 to 80 percent of a typical lead-acid battery is made from recycled lead and plastic.
The plastic in batteries is recycled and reprocessed into other plastic products and battery acid is treated and either disposed of safely into the sewer system or converted into sodium sulfate, a powder used in textile and glass manufacturing and as an ingredient in laundry detergent.
Overall, lead-acid batteries have the highest rate of recycling among all products sold in the USA.
The only time a lead-acid battery ends up in the landfill is through carelessness. Many states impose hefty fines on anybody or any company found disposing of lead-acid batteries incorrectly. Thus, the landfill volume of lead-acid batteries is negligible.
Fortunately, that's one myth that can be considered safely disposed of!
For more about custom manufacturer of VRLA battery products,please visit https://www.bullsbattery.com/